Research
Funded projects
SIRIUS (ERC) – concluded
Placenta (EPSRC) – concluded
EMBOSS (EPSRC) – concluded
SynBIM (EPSRC) – concluded
Research themes
Microfluidics modelling
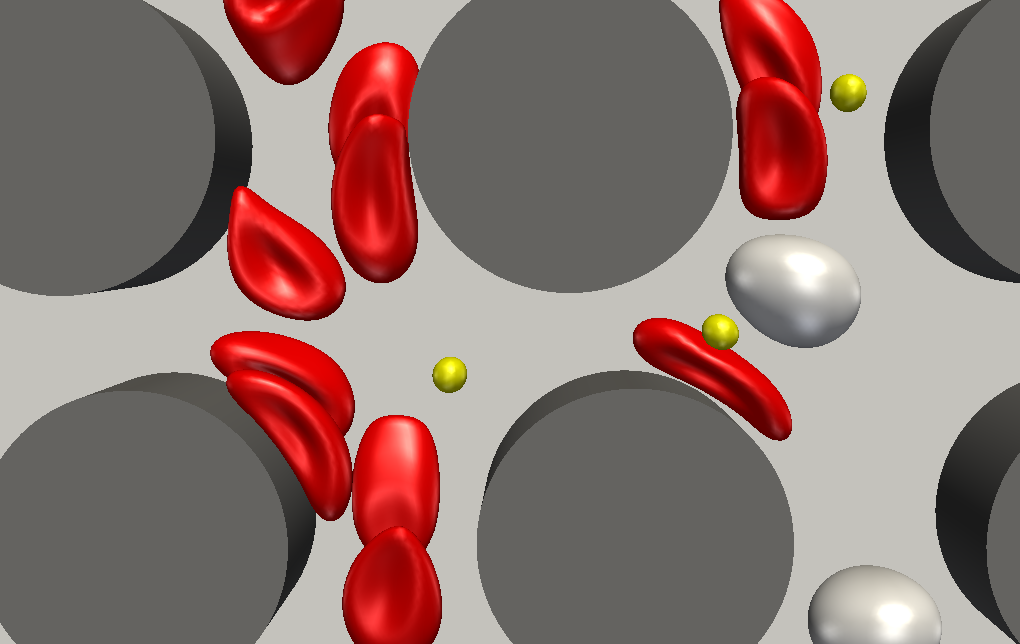
Our group is investigating how microfluidic devices can be designed and employed to characterise and separate particles, most prominently biological particles, such as blood cells, bacteria or cancer cells. The primary applications are lab-on-chip devices for point-of-care diagnostics. This includes deterministic lateral displacement (DLD), inertial microfluidics and other approaches. The challenge is the complex interaction of particle dynamics, device geometry and fluid flow.
Latest publications
- L. Koens, R. Vernekar, T. Krüger, M. Lisicki, D.W. Inglis. The slow viscous flow around doubly-periodic arrays of infinite slender cylinders. IMA J. Appl. Math. 88, 869-887 (2024) arXiv, Oxford Academic
- C. Mallorie, R. Vernekar, B. Owen, D.W. Inglis, T. Krüger. Numerical analysis of flow anisotropy in rotated-square deterministic lateral displacement devices at moderate Reynolds number. Phys. Rev. Fluids 9, 024203 (2024) bioRxiv, PRF
- B. Owen, K. Thota, T. Krüger. Numerical investigation of heterogeneous soft particle pairs in inertial microfluidics. Soft Matter 20, 887 (2024) bioRxiv, Royal Society
- B. Owen, K. Kechagidis, S.R. Bazaz, R. Enjalbert, E. Essman, C. Malorie, F. Mirghaderi, C. Schaaf, K. Thota, R. Vernekar, Q. Zhou, M.E. Warkiani, H. Stark, T. Krüger. Lattice-Boltzmann Modelling for Inertial Particle Microfluidics Applications — A Tutorial Review. Adv. Phys. X 8:1 (2023) bioRxiv, T&F Online
- K. Kechagidis, B. Owen, L. Guillou, H. Tse, D. Di Carlo, T. Krüger. Numerical investigation of the dynamics of a rigid spherical particle in a vortical cross-slot flow at moderate inertia. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 9, 100 (2023) bioRxiv, Nature
- K. Thota, B. Owen, T. Krüger. Numerical study of the formation and stability of a pair of particles of different sizes in inertial microfluidics. Phys. Fluids 35, 032001 (2023) bioRxiv, AIP
- B. Owen, T. Krüger. Numerical investigation of the formation and stability of homogeneous pairs of soft particles in inertial microfluidics. J. Fluid Mech. 937, A4 (2022) arXiv, JFM
- K.K. Zeming, R. Vernekar, M.T. Chua, K.Y. Quek, G. Sutton, T. Krüger, W.S. Kuan, J. Han. Label-free biophysical markers from whole blood microfluidic immune profiling reveal severe immune response signatures. Small 2006123 (2021) Small
Blood flow modelling
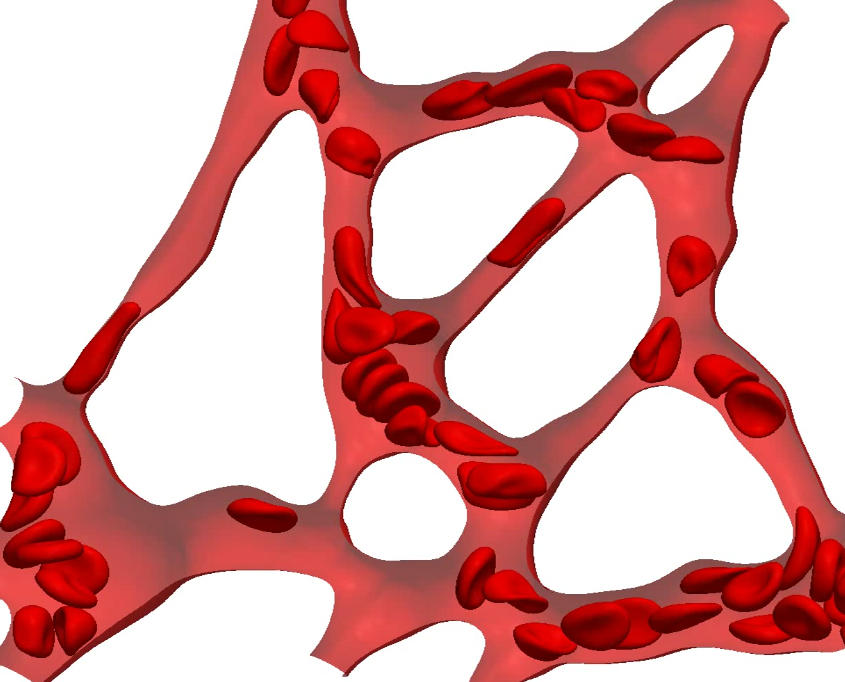
The understanding of blood flow in health and disease is a central research topic in Engineering and Medicine. Typical diseases affecting or affected by blood flow are cancer, hypertension, diabetes and malaria. My group is developing advanced models and software to characterise particulate blood flow in capillary networks, tumour vasculature and the retina. Most of the blood flow modelling in my group is microscopic, which means that blood cells and their flow-induced deformations are resolved. This requires fluid-structure interaction algorithms, such as lattice Boltzmann, finite elements and immersed boundaries.
Latest publications
- H.M. Szafraniec, F. Bull, J.M. Higgins, H.A. Stone, T. Krüger, P. Pearce, D.K. Wood. Suspension physics govern the multiscale dynamics of blood flow in sickle cell disease.Sci. Adv. 12, eadx3842 (2026) bioRxiv, Science
- R. Enjalbert, J. Köry, T. Krüger, M.O. Bernabeu. Abnormal vasculature reduces overlap between drugs and oxygen in a tumour computational model: implications for therapeutic efficacy. PLoS Comput. Biol. 21, e1013801 (2025) bioRxiv, PLoS
- R. Enjalbert, T. Krüger, M.O. Bernabeu. Effect of vessel compression on blood flow in microvascular networks: implications for tumour tissue hypoxia. Commun. Phys. 7, 49 (2024) bioRxiv, Nature
- A. Jötten, A. Schepp, A. Machon, K. Moll, M. Wahlgren, T. Krüger, C. Westerhausen. Survival of P. falciparum infected Red Blood Cell Aggregates in Elongational Shear Flow. Lab Chip 24, 787 (2024) Research Square, Royal Society
- Y. Rashidi, G. Simionato, Q. Zhou, T. John, A. Kihm, M. Bendaoud, T. Krüger, M.O. Bernabeu, L. Kaestner, M.W. Laschke, M.D. Menger, C. Wagner, A. Darras. Red blood cell lingering modulates hematocrit distribution in the microcirculation. Biophys. J. 122, 1526 (2023) bioRxiv, ScienceDirect
- Q. Zhou, K. Schirrmann, E. Doman, Q. Chen, N. Singh, P. Ravi Selvaganapathy, M.O. Bernabeu, O.E. Jensen, A. Juel, I.L. Chernyavsky, T. Krüger. Red blood cell dynamics in extravascular biological tissues modelled as canonical disordered porous media. Interface Focus 12, 20220037 (2022) bioRxiv, Royal Society
- H. Wang, T. Krüger, F. Varnik. Geometry and flow properties affect phase shift between pressure and shear stress waves in blood vessels. Fluids 6(11), 378 (2021) Fluids
- Q. Zhou, T. Perovic, I. Fechner, L.T. Edgar, P.R. Hoskins, H. Gerhardt, T. Krüger, M.O. Bernabeu. Association between erythrocyte dynamics and vessel remodelling in developmental vascular networks. J. R. Soc. Interface 18, 20210113 (2021) bioRxiv, Interface
- R. Enjalbert, D. Hardman, T Krüger, M.O. Bernabeu. Compressed vessels bias red blood cell partitioning at bifurcations in a hematocrit-dependent manner: Implications in tumor blood flow. PNAS 118, e2025236118 (2021) bioRxiv, PNAS
- Q. Zhou, J. Fidalgo, M.O. Bernabeu, M.S.N. Oliveira, T. Krüger. Emergent cell-free layer asymmetry and biased haematocrit partition in a biomimetic vascular network of successive bifurcations. Soft Matter 17, 3619-3633 (2021) Soft Matter
Complex flow modelling
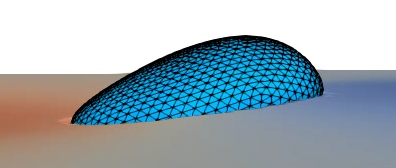
There is no unique and clear definition of “complex flows”. It can be understood as a research field involving fluid flow coupled with additional physical mechanisms, such as diffusion, surface tension (capillary effects), phase change (e.g. boiling) and particle growth/precipitation out of solution. In the BioFM group, the unifying element is the lattice-Boltzmann method (see our book).
Latest publications
- M. Pepona, A. Shek, C. Semprebon, T. Krüger, H. Kusumaatmaja. Modelling ternary fluids in contact with elastic membranes. Phys. Rev. E 103, 022112 (2021) arXiv, PRE
- M. Wouters, O. Aouane, T. Krüger, J. Harting. Mesoscale simulation of soft particles with tunable contact angle in multi-component fluids. Phys. Rev. E 100, 033309 (2019). arXiv, PRE